Oracle Cloud Infrastructure is a comprehensive and unified platform that provides various services such as IaaS, PaaS, SaaS, and DaaS. It can be said that OCI is an ideal solution for businesses that want to switch from on-premise systems to the cloud. Join Benefits Of Oracle Analytics Cloud to learn about the services that OCI provides as well as the benefits that OCI brings to businesses.

Services offered by Oracle Cloud
1. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
OCI’s computing capabilities range from physical servers and virtual machines (VMs) to graphics processing units (GPUs), high-performance computing (HPC), and container orchestration. OCI has different storage options including local, file, object, and repository for high-volume and mission-critical storage use cases.
OCI is designed with a focus on network-independent virtualization. OCI’s network virtualization capabilities decouple the custodian’s network, significantly reducing the security risk underlying most monitors.
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
OCI’s PaaS builds on IaaS services, integrating Oracle and other open-source frameworks. Some of OCI’s popular PaaS offerings include:
Application development, where developers can design, code, test, and deploy modern intelligent applications in the cloud
The cloud database, where organizations can access high-performance versions of Oracle Autonomous Database, reduces the workload to manage.
Content management, where organizations can personalize customer experiences quickly through a unified, centralized tool.
Integration, where developers can integrate different apps and data from different sources to create insightful analytics.
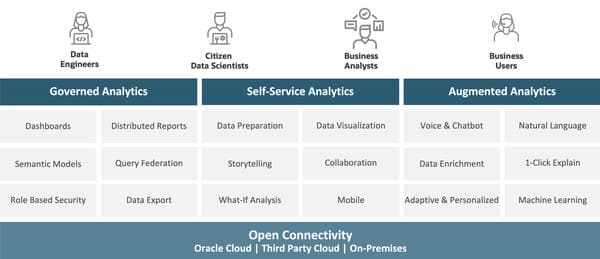
Business Analytics, where organizations can gain comprehensive business intelligence (BI) on their data through embedded machine learning algorithms.
3. Software as a Service (SaaS)
OCI SaaS services are applications that are always ready to be used and can be easily leveraged by businesses for different use cases. Examples include automating various activities, including human resources, enterprise resource planning (ERP), sales and marketing, supply chain management, and financial management.
4. Data as a Service (DaaS)
OCI’s DaaS is a data aggregator. Users can leverage this tool to access more than 135 million contact records worldwide with more than 90 different business attributes (firmographics). Also, use the data in it to normalize and correct contact data in real time. In addition, DaaS provides data completely and accurately for each business.
Benefits of Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI)
Thanks to technologies like Autonomous Database, Automated Data Warehouse, and Oracle Autonomous Transaction Processing, OCI is capable of handling large, data-intensive workloads with better security. Oracle cloud infrastructure offers businesses the following benefits:

1. Ability to build on top of on-premise solutions
Businesses that have invested heavily in on-premise solutions can move them to the cloud easily with full control e.g. virtualization, server and storage setup, and data center location Whether. At the same time, businesses have the option to use Oracle expertise when needed.
2. Performance Boost
Businesses of any size need applications that are constantly being updated. Oracle cloud infrastructure provides simple servers that can process huge data sets in real-time. Leverage high-performance, highly scalable Oracle databases and related technologies such as Oracle Real Applications Clusters. These servers also use fast memory (NVME) with the ability to process several tens of terabytes per instance.
3. High Security
Businesses need highly secure applications, networks, and data to avoid potential breaches that affect their reputation. Oracle cloud infrastructure is built with a special focus on security:
- Separation of network and computing resources
- Allows you to set up advanced protection through the built-in firewall
- Integration with identity access management tools
- Multi-Factor Authentication
- Data encrypt
4. Open Architecture
With Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, businesses will not be required to use a single vendor solution. Enterprises can run workloads on Oracle or another platform while maintaining interoperability through standards compliance. Additionally, OCI supports open-source technology and programming languages with the ability to integrate DevOps and IT tools from different vendors and runs on both Windows and Linux servers.
Oracle Automated Database (OAD)
Oracle Automated Database (OAD) is a cloud-based database with machine learning (ML) capabilities. Database with ultimate self-care, minimizing database administrator (DBA) intervention, and eliminating error-prone manual tasks.
The “self-driving” aspect of OAD helps DBAs cut out of the usual mundane tasks and focus instead on higher-level and more developed work. The focus of OAD performance is on adaptive ML algorithms with the ability to automatically patch, backup, tune, and upgrade the database at any time while the system is running to ensure maximum availability.
Oracle launched OAD in 2017, starting with Oracle Database 18c and later versions. As a database management software, Oracle 18c is not yet capable of high automation. The automation features were then built by Oracle on Oracle 18c to turn it into an automation database. Oracle offers this combination as a cloud service, which is described with three main elements as “self-driving”, “self-securing” and “self-repairing”. repair.

Self-driving: OAD automates all database operations, including provisioning, monitoring, backup, tuning, and optimization. However, this does not mean that OAD will eliminate the role of the DBA. A DBA is needed in managing some database tasks such as connecting an application to a database.
Self-securing: OAD has built-in capabilities to protect itself against attacks by internal or external users. Enterprises can leverage OAD to reduce security concerns and database patching and encryption issues.
Self-repairing: OAD has self-healing protection mechanisms against planned and unplanned downtimes. As a result, you can quickly and automatically recover from a crash without any downtime.
OAD consists of two main components with the ability to tailor it to and seamlessly with different types of workloads: data warehousing and transaction processing. Data warehouses use prepared data to perform business intelligence operations. Concurrently manage all database management lifecycle activities, including query scanning.
On the other hand, transaction processing facilitates time-based transactions such as real-time analytics and personalization, users will need less records based on predefined activities.
One of the first benefits that businesses receive from OAD is the ability to save costs. By reducing the number of DBAs to manage OAD or redeploying them elsewhere into more strategic functions, businesses can save costs.
The next benefit OAD can bring to businesses is the ability to raise service levels by eliminating error-prone, manual database operations through automation. The transition to OAD allows DBAs to refocus their data science skills into deeper insights that deliver more value to the business.
With OAD, businesses can achieve maximum performance, uptime database and always secure. Unlike traditional databases, OAD leverages machine learning algorithms, designed for automatic performance tuning and real-time auto-patching. This ensures maximum performance and security for your business.

